Cephalexin With or Without TMP-SMX Showed Similar Efficacy for Uncomplicated Cellulitis
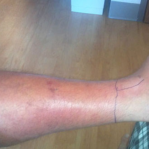
A recent multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of cephalexin alone or in combination with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) for treatment of acute uncomplicated cellulitis in the outpatient setting. Clinical cure rates were similar between the combination therapy arm (83.5%) and the monotherapy arm (85.5%). Adverse event rates and secondary outcomes (including overnight hospitalization, recurrent skin infections, and similar infection in household contacts) were not different between treatment arms.
For additional details, please read Moran GJ, et al. JAMA 2017;317(20):2088-96.



