NHSN Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Module Reporting – CMS required by 2024!

NHSN Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Module Reporting – CMS required by 2024!
Antibiotic Awareness Week 2022
Antimicrobial resistance rates continue to increase in hospitals across the United States.1 One of the five CDC core actions to combat the spread of antimicrobial resistance is improving the use of antimicrobials.2 Studies show that providing timely and reliable feedback of information to clinicians regarding their prescribing practices, such as through antimicrobial usage reports, can improve appropriateness of antimicrobial use.3-4
Purpose
The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) is a secure, Internet-based surveillance system that expands and integrates patient and healthcare personnel safety surveillance systems. Facilities that participate in certain reporting programs operated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) can do so through use of NHSN. Many hospitals currently use NHSN to report bloodstream Infections (CLABSI – Central line-associated bloodstream infection), urinary tract infections (CAUTI – Catheter-associated urinary tract infection), ventilator-associated events (VAE), and Surgical Site Infections (SSI).
The NHSN AUR Module provides a mechanism for facilities to report and to analyze antimicrobial use and/or resistance data to inform benchmarking, reduce antimicrobial resistant infections through antimicrobial stewardship, and interrupt transmission of resistant pathogens at individual facilities or facility networks.5
NHSN Antimicrobial Use (AU) Option
 The Antimicrobial Use (AU) Option of the CDC ’s NHSN is a surveillance resource that can provide actionable data for antibiotic stewardship programs. The data can be used to measure AU across hospitals and before, during, and after stewardship interventions. The NHSN AU data, in addition to other data sources, were used to characterize antibiotic use during the COVID-19 pandemic to identify opportunities for improvement. More than 2,400 acute care hospitals across the United States have submitted at least one month of data to the AU Option as of August 2022. Of those hospitals, 2,283 reported in the past 12 months (July 2021 – June 2022).
The Antimicrobial Use (AU) Option of the CDC ’s NHSN is a surveillance resource that can provide actionable data for antibiotic stewardship programs. The data can be used to measure AU across hospitals and before, during, and after stewardship interventions. The NHSN AU data, in addition to other data sources, were used to characterize antibiotic use during the COVID-19 pandemic to identify opportunities for improvement. More than 2,400 acute care hospitals across the United States have submitted at least one month of data to the AU Option as of August 2022. Of those hospitals, 2,283 reported in the past 12 months (July 2021 – June 2022).
As of 2021, only 13 of 54 (24%) eligible facilities in Nebraska report antibiotic use data to NHSN.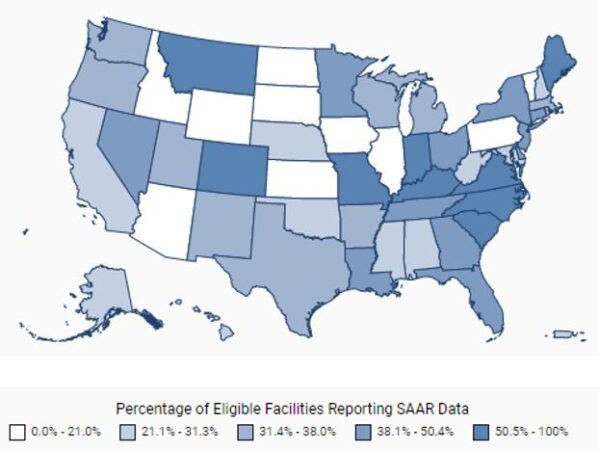
The growth in voluntary reporting suggests that hospitals are finding benefits in reporting and using this data. This growth, coupled with the growing recognition of the importance of national data on hospital antibiotic use and resistance prompted the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to include a requirement for this reporting in their fiscal year 2023 Inpatient Prospective Payment System final rule.
Reporting antimicrobial use and resistance data will be included in the Public Health and Clinical Data Exchange Objective as a required measure beginning with the EHR reporting period in CY 2024.
Standardized Antimicrobial Administration Ratio (SAAR)
One output measure included in NHSN’s AU Option of the Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR Module) is the Standardized Antimicrobial Administration Ratio (SAAR). The SAAR is a risk-adjusted benchmarking measure of antibiotic use that can help inform stewardship efforts by enabling hospitals to see how their antibiotic use compares to other facilities. The 2021 NHSN AU Option Report provides a summary of SAAR distributions and percentages of use within the SAAR antimicrobial agent categories in adult, pediatric and neonatal patient care locations. Data on inpatient antibiotic use is available on the CDC’s Antibiotic Resistance & Patient Safety Portal.
Getting started
The first step in beginning to upload data to the AU/AR option is to evaluate your facility’s software. Several software vendors have developed reporting mechanisms for facilities to report antimicrobial use and/or resistance data. The NHSN AU Option does not allow manual data entry due to the amount of data submitted each month. Facilities may be able to report through their primary EMR system or through their clinical decision support software. Check this list to see if your facility’s software vendor is included – AU SDS Vendors | NHSN | CDC
The complete manual for the Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) module can be found at 2022 NHSN AUR Protocol (cdc.gov) and a summary of Frequently Asked Questions can be found at FAQs: Antimicrobial Use (AU) Option | NHSN | CDC
 Written by Jenna Preusker, Pharm.D., BCPS
Written by Jenna Preusker, Pharm.D., BCPS
Nebraska ASAP Pharmacy Coordinator
References
- Weiner LM, Webb AK, Limbago B, et al. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with adult healthcare-associated infections: summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2015-2017. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2020;41:1-18.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threatsreport-508.pdf.
- Davey P, Marwick CA, Scott CL, et al. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices for hospital inpatients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017:2;CD003543.
- Ansari F, Gray K, Nathwani D, et al. Outcomes of an intervention to improve hospital antibiotic prescribing; interrupted time series with segmented regression analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003;52:842-8
- Barlam TF, Cosgrove SE, Abbo LM, et al. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016 May 15;62(10):e51-77. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw118. Epub 2016 Apr 13. PMID: 27080992; PMCID: PMC5006285.



