Ambulatory Care
Close to 62% of overall antibiotic expenditure is associated with the outpatient setting, exceeding those in the inpatient (33.6%) and long-term care (4.9%) settings combined. As much as half of all antibiotic prescriptions written in the outpatient setting might be inappropriate due to unnecessary antibiotic prescribing or selection of less than optimal antibiotic, dose, and/or duration.
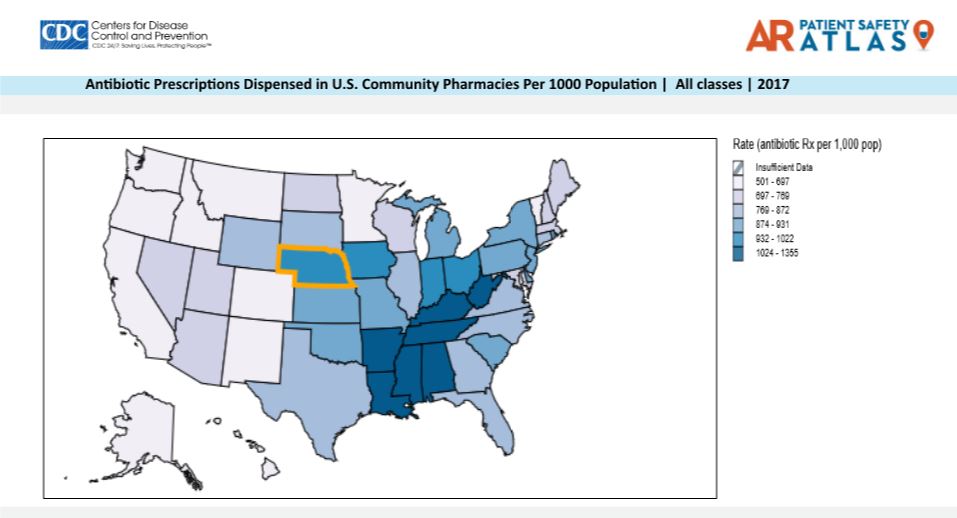
According to data from the CDC, Nebraska has consistently prescribed more antibiotics annually in the outpatient setting compared to the national average in 2011 to 2017. In 2017, Nebraska ranked number 8 in outpatient antibiotic prescriptions. Appropriate prescribing was estimated to be at the 50th percentile.
Antibiotic use is not without harm. It is estimated that more than 140,000 emergency department visits annually are associated with adverse events from outpatient antibiotic use. These adverse events included more commonly encountered reactions such as rash and diarrhea to ones that are less common but potentially life-threatening such as severe allergic reactions. In addition, antibiotic overuse is associated with antibiotic resistance that can result in higher morbidity and mortality. Because of these reasons and as a matter of patient safety, it is prudent to prescribe antibiotics only when necessary in all healthcare settings, and especially in the outpatient setting where most of the antibiotic prescribing occurs.
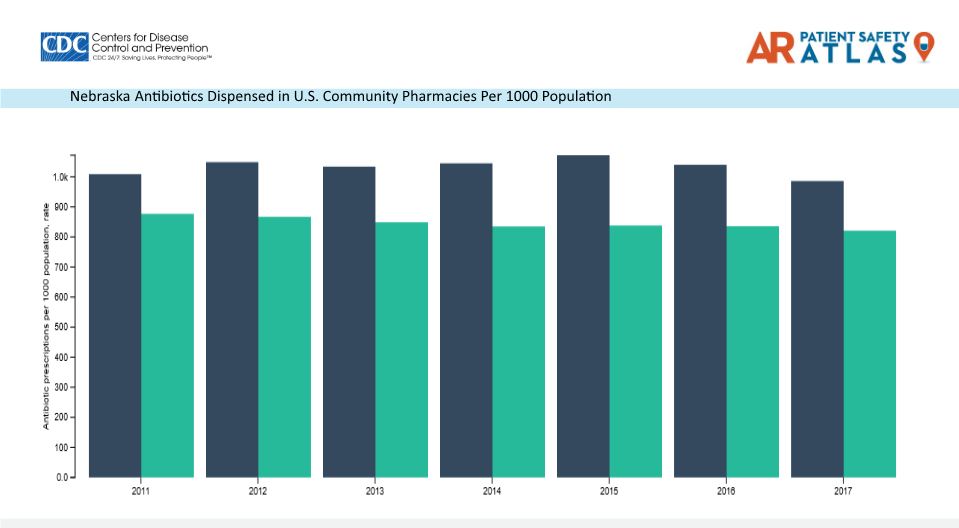
On a brighter note, outpatient antibiotic prescriptions filled in community pharmacies in Nebraska decreased to 986 prescriptions per 1,000 population in 2017, dipping below 1,000 per 1,000 population for the first time this decade. Even though antibiotic prescribing and use have improved in Nebraska, continued efforts in antibiotic stewardship to further improve in this area is necessary.
The prescriber and patient education materials and tools provided in this section will facilitate more appropriate antibiotic prescribing in the outpatient setting. Click on one of the sections to the right to access these materials.



